Shipping zones: How to design an effective strategy

In the zone or out of zone? When it comes to ecommerce shipping, knowing how shipping zones affect the cost of each delivery is a major consideration. Where you ship from, how you ship, and which shipping service you use will have a major impact on how shipping zones influence the shipping rates you pay.
We’re going to dive into how shipping zones work for domestic shipments, how carriers use shipping zones to calculate rates, and how you can create an effective shipping zone strategy.
What are shipping zones?
Shipping zones or postal zones refer to numbered geographic regions that shipping carriers use to calculate shipping rates and transit times throughout the domestic U.S. and internationally. Major shipping carriers use shipping zones to determine the transit time, fuel costs, and other operational costs required to deliver a package from point A to point B. So, the further a package needs to travel from its point of origin to the end destination, the higher the shipping cost.
The purpose of shipping zones is to simplify cost calculations for carriers and shippers. By categorizing different regions into zones, it’s easier to understand how shipping rates are calculated and the total transportation costs the carrier needs to shoulder. The more shipping zones that are being crossed, the more it costs the carrier and the more that the shipper has to pay.
How do shipping zones affect shipping costs?
Shipping zones affect costs considerably for ecommerce shippers, especially when shipping over long distances, such as coast to coast or outside of the U.S. mainland.
Distance to ship
The point of origin and destination zone determine the number of shipping zones that a package will travel through, and in turn the overall shipping cost. Longer distances will result in higher shipping costs, and typically longer transit times, depending on the service level.
Carrier-specific shipping zone maps
Every parcel carrier uses its own shipping zone system, which can vary based on whether they are a nationwide or regional carrier and how many distribution centers a parcel needs to pass through to reach its destination. The difference in how carriers determine shipping zones means that the cost to ship a package with one carrier may differ significantly from another. Understanding shipping zones as they are defined by each carrier is important to make informed decisions about which carrier to use.
However, shipping zones aren’t the only factors involved in calculating shipping costs. Other factors that contribute to shipping fees include:
Dimensional weight
Packages with a high DIM weight, such as oversized packages or small, heavy parcels, will cost more to ship because they take up more space in delivery vehicles, especially over long distances. If packages require manual sorting and handling, they will also accumulate more accessorial charges during their shipment between zones, which pushes up shipping costs.
Service Level
The speed of delivery i.e. economy ground services vs. priority mail express, has a huge bearing on overall shipping costs. While the number of shipping zones being crossed is the same, expedited delivery speeds will affect what delivery options are available.
Shipping zone charts compared
All major U.S. shipping carriers use shipping zone calculations as a way to determine shipping rates. The distance to ship is a primary consideration when charging for shipping services, with the lowest-numbered zones representing shorter transit distances, and higher zones representing the furthest distances from the point of origin or origin zip code. UPS, FedEx, and USPS all use similar distance measures to calculate shipping zones and create shipping zone maps:
Zone 1: 50 mile radius
Zone 2: 51 – 150 mile radius
Zone 3: 151 – 300 mile radius
Zone 4: 301 – 600 mile radius
Zone 5: 601 – 1,000 mile radius
Zone 6: 1,001 – 1,400 mile radius
Zone 7: 1,401 – 1,800 mile radius
Zone 8: 1,801+ mile radius
Zone 9: Non-Mainland US Regions
In sum, a delivery that’s taking place within a 50-mile radius will be billed as a zone 1 delivery, as the origin and destination zip codes remain within the same shipping zone. But if the destination zone is a 500 mile radius from the point of origin, this would be classed as a zone 4 delivery and will cost considerably more due to the longer distance and high associated delivery costs.
FedEx shipping zones
FedEx divides the U.S. into zones ranging from zone 2 to zone 8. Zone 2 represents local deliveries which can be completed in one day, while zone 8 represents the farthest distances which take 7+ days to complete delivery.
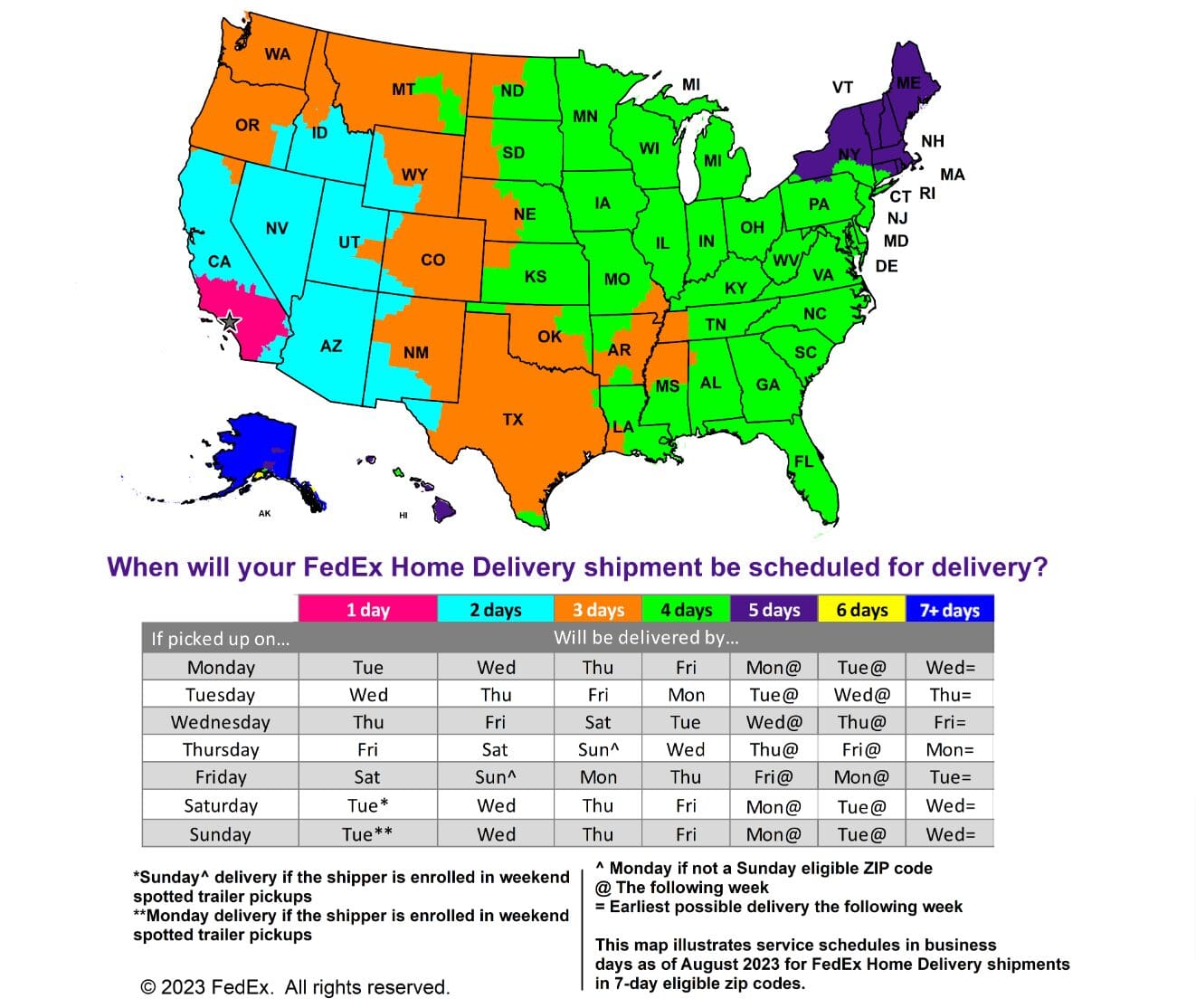
FedEx shipping zone map with the origin zip code set in the Greater Los Angeles area.
UPS Shipping zones
Similarly to FedEx, UPS shipping zones range from 2 to 8, depending on the originating zone for domestic shipment.
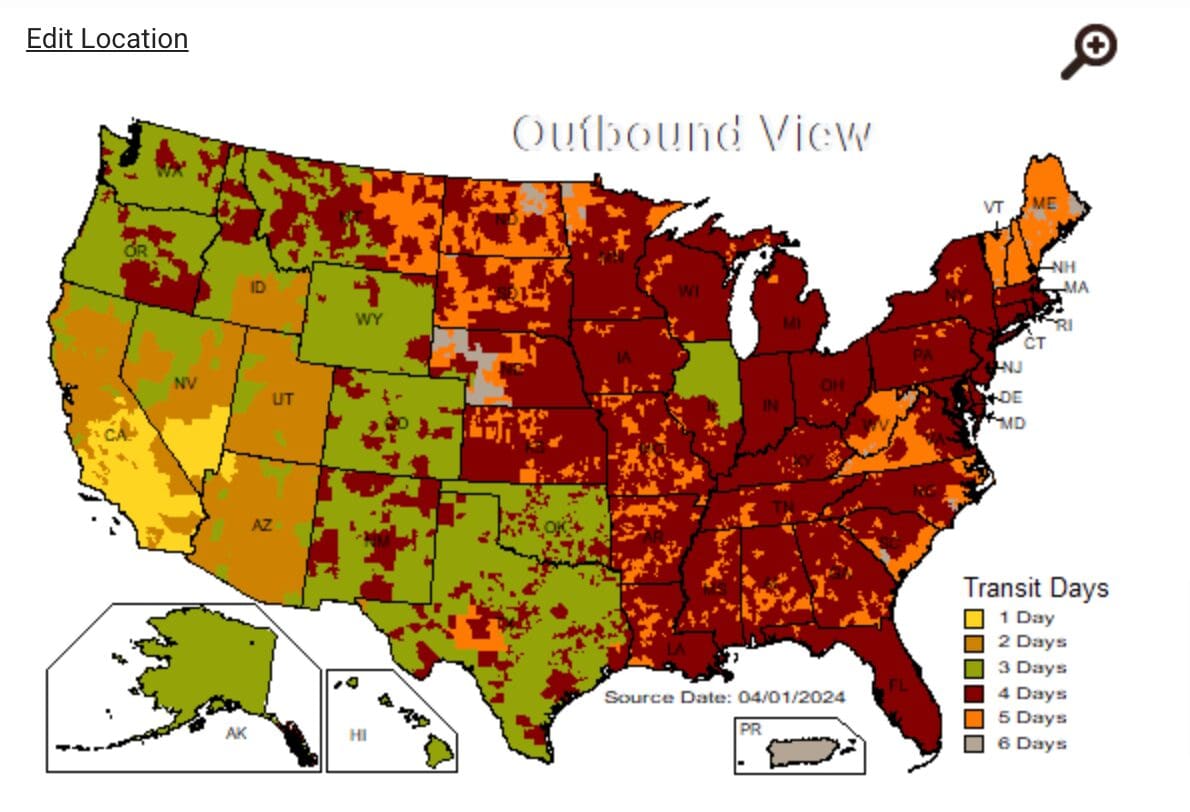
UPS shipping zone map with the point of origin set in the Greater Los Angeles area.
USPS shipping zones
The United States Postal Service divides the country into zones ranging from 1 to 9, with the zone number increasing with the distance from the point of origin. USPS has a handy ‘zip code pair’ tool on its website for determining shipping zones for any particular delivery.
How to optimize your zone shipping strategy
Compare shipping rates between carriers
Shipping zone maps between carriers will result in lower shipping costs for certain shipments, especially when shipping locally rather than long distances. By rate shopping between carriers, ecommerce businesses can often net significant cost savings, rather than sticking with the same carrier for all deliveries.
Zone skipping
Zone skipping is when an ecommerce business consolidates shipments according to the destination zone, rather than shipping each order individually. Once the consolidated load arrives at the final shipping zone, packages are split up and sent on using local delivery services. By shipping packages in bulk, each parcel will ‘skip’ shipping zones and reduce shipping costs.
Another bonus is that consolidated shipments are sent directly to regional hubs or distribution centers, meaning there are fewer transit points where packages need to be sorted or checked. This results in fewer additional handling fees or accessorial charges, which also lowers shipping costs.
Flat-rate shipping
Flat-rate shipping helps ecommerce businesses to reduce shipping zones by pricing shipments according to dimensional weight, rather than the distance the package is traveling. This is a good strategy for businesses that are regularly shipping packages that are similar in size and weight, as it helps to standardize shipping processes for the same package type, regardless of the destination zone.
Regional carriers
Regional carriers are postal services that only operate within a defined geographic area, rather than shipping nationwide or internationally. Because they specialize in local delivery services, they are considerably cheaper for short-haul deliveries in a zone 1 or 2 radius, rather than using a national carrier.
Choosing the right service level
Choosing a fast shipping service for a long transit distance can prove very costly for shippers, as it may require expensive air shipping to reach zip codes in zone 7 or 8. By selecting a slow shipping method for longer shipments or offering free shipping promotions, you can save money on shipments that need to travel through multiple different zones to reach the end customer.
Use multiple fulfillment centers
Storing inventory in more than one location enables ecommerce businesses to avoid costly, cross-country shipments that need to cross multiple shipping zones to reach their final destination. For example, having fulfillment centers in different regions to cover local customer orders means that each parcel only needs to cross one or two zones, rather than several. Multi-node fulfillment also dramatically lowers delivery costs by shortening transit times to the end customer, which also boosts customer satisfaction.
Efficient Zone Shipping with ShippingTree
Automated rate shopping
ShippingTree’s advanced rate-shopping technology helps merchants streamline their shipping by selecting the best rates based on customizable preferences. Whether prioritizing speed or cost, you can tailor shipping rules to fit your strategy, with options to choose carriers, transit times, and delivery priorities.
Nationwide fulfillment network
ShippingTree’s network of strategically located warehouses—in cities like Columbus, Los Angeles, and Dallas—enables fast two-day and even same-day delivery. With real-time tracking through the ShippingTree app, retailers gain complete visibility and control across all locations.
Contact us today to discover how ShippingTree can transform your shipping strategy.



